Introduction-Building a Reliable Gamepad Tester Tool
Have you ever wondered why your gaming controller sometimes behaves erratically during intense gameplay? Or why certain buttons seem unresponsive at the worst possible moments?
Behind every smooth gaming experience lies a critical piece of software that many gamers never think about: the gamepad tester tool.
For developers, building a reliable online controller tester is far more complex than it appears on the surface. It requires deep understanding of hardware communication protocols, browser APIs, cross-platform compatibility, and user experience design.
This comprehensive guide pulls back the curtain on gamepad testing tool development. We’ll explore real lessons from developers who have tackled the challenges of creating USB controller testers, joystick calibration systems, and comprehensive button check utilities.
Whether you’re a developer looking to build your own gamepad test application or a curious gamer wanting to understand how these tools work, you’ll find valuable insights in the sections ahead.
Related Post: XInput vs DirectInput Explained: Understanding Gamepad Input APIs
Table of Contents
Why Gamepad Testing Tools Matter
Gamepad testing tools serve a crucial role in the gaming ecosystem. They bridge the gap between hardware manufacturers and end users, providing essential diagnostic capabilities.
The Growing Need for Controller Diagnostics
The gaming peripheral market has exploded in recent years. With dozens of controller manufacturers producing hundreds of different models, compatibility issues have become increasingly common.
Gamers need reliable ways to:
- Verify their controller is functioning correctly
- Diagnose button response issues
- Check for joystick drift problems
- Test trigger sensitivity and accuracy
- Validate wireless connection stability
Professional vs. Consumer Applications
Professional game developers use sophisticated gamepad testing suites during development. These tools help ensure their games properly support various controller configurations.
Consumer-facing tools, like web-based controller testers, serve different purposes:
- Quick hardware verification
- Troubleshooting connection issues
- Calibration validation
- Pre-purchase testing of used controllers
Internal link suggestion: Link to guide on “How to Test Your Controller Before Buying Used”
Understanding the HTML5 Gamepad API

The HTML5 Gamepad API revolutionized browser-based controller testing. It provides a standardized way for web applications to interact with gaming controllers.
How the Gamepad API Works
The Gamepad API operates through event-driven architecture. When a controller connects, the browser fires a gamepadconnected event. Similarly, disconnection triggers gamepaddisconnected.
Here’s what developers need to understand:
Key API Methods:
navigator.getGamepads()– Returns an array of connected controllers- Gamepad object properties include buttons, axes, id, and mapping
- Continuous polling is required for real-time input reading
Standard Mapping vs. Non-Standard Controllers
The API defines a “standard” gamepad mapping that corresponds to modern console controllers. This includes:
- 17 buttons (face buttons, shoulders, triggers, sticks, D-pad, menu buttons)
- 4 axes (two analog sticks, each with X and Y)
However, many controllers don’t conform to this standard mapping. Developers must account for these variations in their gamepad test applications.
Browser Support Considerations
Not all browsers implement the Gamepad API identically. Chrome, Firefox, and Edge offer robust support. Safari’s implementation has historically lagged behind.
Developers building cross-platform online controller testers must implement fallback mechanisms and browser-specific workarounds.
Core Components of a Reliable Controller Tester
Building a comprehensive gamepad tester requires several interconnected components working harmoniously together.
Input Detection Layer
The input detection layer continuously monitors controller state changes. It must:
- Poll controller inputs at consistent intervals
- Detect button presses with minimal latency
- Track analog stick positions accurately
- Handle multiple simultaneous inputs
Data Processing Engine
Raw input data requires processing before display. This includes:
- Normalization: Converting axis values to consistent ranges (-1 to 1)
- Filtering: Removing noise from analog inputs
- Threshold detection: Determining when inputs should register as active
Visualization Module
Users need clear, intuitive visual feedback. Effective visualization includes:
- Real-time button state indicators
- Analog stick position displays
- Trigger pressure gauges
- Input history logs
Configuration System
Advanced users expect customization options:
- Dead zone adjustments
- Sensitivity curves
- Button remapping displays
- Threshold configurations
Handling Different Controller Types
One of the biggest challenges in gamepad testing tool development is supporting the vast array of controller types available.
Xbox Controller Testing
Xbox controllers enjoy excellent support across platforms. They typically map correctly to the standard gamepad layout.
Key testing considerations include:
- Trigger analog precision (important for racing games)
- Bumper response times
- Xbox button functionality in different contexts
- Wireless vs. wired connection differences
PlayStation Controller Support
DualShock and DualSense controllers present unique challenges. The touchpad, adaptive triggers, and haptic feedback require special handling.
Testing features specific to PlayStation controllers:
- Touchpad position and gesture recognition
- Light bar color control verification
- Motion sensor (gyroscope/accelerometer) testing
- Pressure-sensitive buttons (older DualShock models)
Nintendo Controller Compatibility
Nintendo’s Joy-Con and Pro Controllers have their own quirks. Developers must account for:
- Joy-Con’s unique button placement
- Motion control functionality
- NFC reader for amiibo (where applicable)
- HD rumble verification
Third-Party and Generic Controllers
Generic USB controller testers face the biggest challenge with third-party devices. These controllers may:
- Report incorrect button mappings
- Provide inconsistent axis ranges
- Lack proper driver support
- Use non-standard communication protocols
External source suggestion: Link to W3C Gamepad API specification for technical reference
Detecting and Measuring Controller Drift
Joystick drift detection is one of the most requested features in modern gamepad testers. This section explores how developers implement reliable drift testing.
What Causes Controller Drift?
Understanding drift helps developers build better detection systems. Common causes include:
- Potentiometer wear in analog sticks
- Debris accumulation under stick mechanisms
- Internal component degradation
- Calibration data corruption
Measuring Drift Accurately
Accurate Xbox controller drift test and PlayStation stick drift detection requires sophisticated measurement techniques.
Static Drift Detection:
When the analog stick is at rest, it should report exactly (0, 0). Any deviation indicates potential drift.
Dynamic Drift Analysis:
Monitoring stick behavior during movement reveals:
- Return-to-center accuracy
- Directional bias patterns
- Intermittent drift spikes
Implementing Drift Visualization
Effective drift visualization helps users understand their controller’s health:
- Heat maps showing stick position over time
- Deviation graphs displaying drift magnitude
- Threshold indicators highlighting problematic levels
- Historical comparison tracking drift progression
Implementing Dead Zone Configuration
Dead zone configuration is essential for both testing and practical controller use. Proper implementation requires careful consideration.
Understanding Joystick Dead Zones
A dead zone is a region around the analog stick’s center where small movements are ignored. This prevents unintended inputs from minor stick drift.
Default Dead Zone Considerations:
- Too small: Drift causes unwanted movement
- Too large: Reduces precision and responsiveness
- Optimal: Balances drift prevention with sensitivity
Circular vs. Square Dead Zones
Developers must choose between dead zone shapes:
Circular Dead Zones:
- More intuitive for users
- Equal sensitivity in all directions
- Industry standard approach
Square Dead Zones:
- Easier to implement mathematically
- Can cause directional inconsistencies
- Less common in modern tools
User-Adjustable Dead Zone Controls
Quality gamepad testers provide adjustable dead zone settings:
- Slider controls for size adjustment
- Real-time preview of dead zone effects
- Per-stick configuration options
- Profile saving and loading
Real-Time Input Visualization Techniques
Visualization transforms raw controller data into understandable information. Effective techniques enhance the testing experience significantly.
Button State Indicators
Clear button indicators should:
- Change color instantly on press
- Show pressure values for analog buttons
- Indicate held vs. tapped states
- Support colorblind-friendly designs
Analog Stick Displays
The most common analog stick visualization uses a circular area with a movable dot representing stick position.
Advanced Visualization Options:
- Position trails showing movement history
- Velocity indicators
- Precision measurement overlays
- Grid lines for accuracy assessment
Trigger and Pressure Visualization
Analog triggers require specialized displays:
- Progress bars showing pressure levels
- Numerical percentage indicators
- Response curve graphs
- Activation threshold markers
Input History and Logging
Serious testing requires input logging capabilities:
- Timestamp for each input event
- Button/axis identification
- Value at time of event
- Duration of button holds
Cross-Browser Compatibility Challenges
Building a web-based controller tester that works everywhere is surprisingly difficult.
Chrome-Specific Considerations
Chrome offers the most complete Gamepad API implementation. However, developers must consider:
- Security restrictions on API access
- Tab visibility effects on polling
- Extension interference possibilities
Firefox Differences
Firefox handles some aspects differently:
- Axis value precision variations
- Button indexing differences for non-standard controllers
- Unique permission requirements
Safari Limitations
Safari has historically lagged in Gamepad API support:
- Later adoption of API features
- WebKit-specific bugs
- iOS Safari additional restrictions
Edge and Chromium Browsers
Edge now uses Chromium, simplifying compatibility. But legacy Edge versions may still need consideration for some user bases.
Best Practices for Cross-Browser Support:
- Feature detection before API usage
- Graceful degradation when features unavailable
- Clear messaging about browser compatibility
- Regular testing across browser versions
Performance Optimization Strategies
A laggy controller tester defeats its purpose. Performance optimization is critical for reliable testing.
Efficient Polling Implementation
Polling frequency affects both accuracy and performance:
- 60Hz polling suits most applications
- Higher rates (120Hz+) for precision testing
- RequestAnimationFrame for smooth updates
- Web Workers for heavy processing
Minimizing DOM Manipulation
Frequent DOM updates cause performance issues:
- Use CSS transforms for positioning
- Batch DOM updates when possible
- Consider Canvas or WebGL for complex visualizations
- Implement virtual DOM techniques
Memory Management
Long testing sessions can cause memory issues:
- Limit input history size
- Clear unused data structures
- Implement efficient data storage
- Monitor for memory leaks
Testing Methodology and Quality Assurance
Building a reliable testing tool requires rigorous testing of the tool itself.
Hardware Testing Matrix
Developers should test with diverse hardware:
| Controller Type | Wired | Wireless | Bluetooth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xbox Series | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Xbox One | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| DualSense | ✓ | – | ✓ |
| DualShock 4 | ✓ | – | ✓ |
| Switch Pro | ✓ | – | ✓ |
| Generic USB | ✓ | – | – |
Automated Testing Approaches
Automated tests ensure consistent quality:
- Mock gamepad objects for unit testing
- Integration tests with simulated inputs
- Performance benchmarks for optimization
- Regression testing for browser updates
User Acceptance Testing
Real users provide invaluable feedback:
- Beta testing programs
- Community feedback integration
- Accessibility testing
- Usability studies
User Experience Design Principles
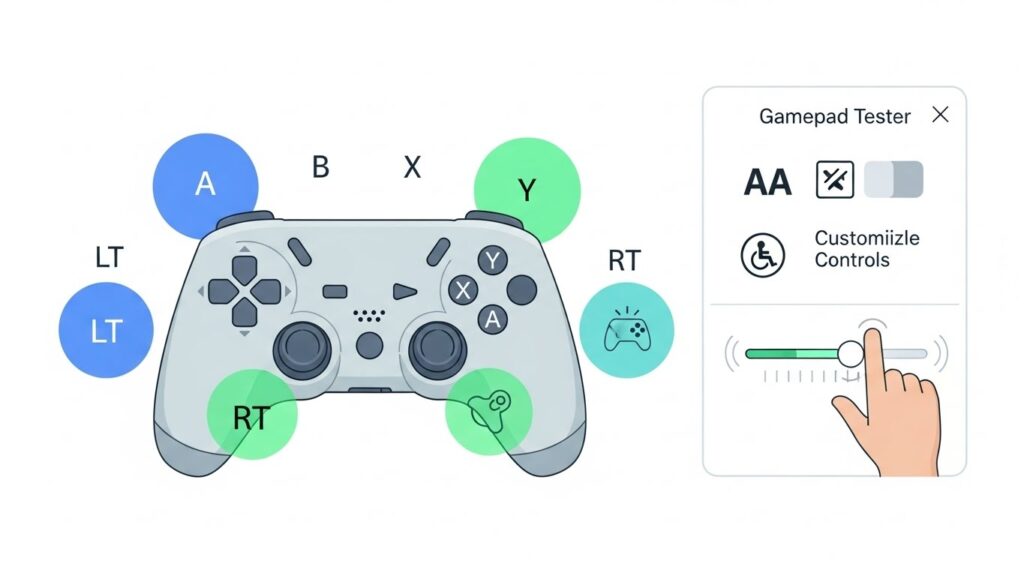
Technical excellence means nothing if users can’t understand the tool.
Intuitive Interface Design
Effective gamepad tester interfaces share common traits:
- Visual controller representation matching user’s hardware
- Clear labeling of all buttons and axes
- Logical information hierarchy prioritizing essential data
- Responsive design for various screen sizes
Accessibility Considerations
Accessible design benefits all users:
- Color choices for colorblind users
- Keyboard navigation support
- Screen reader compatibility
- High contrast mode options
Progressive Disclosure
Don’t overwhelm new users:
- Basic testing visible immediately
- Advanced features behind clear options
- Tutorial overlays for first-time users
- Contextual help throughout
Internal link suggestion: Link to “Complete Guide to Controller Calibration”
Common Development Pitfalls to Avoid
Learn from others’ mistakes to save development time and frustration.
Pitfall 1: Ignoring Edge Cases
Many controllers behave unexpectedly:
- Some report button counts incorrectly
- Axis ranges may not be -1 to 1
- Connection events can fire multiple times
Solution: Build defensive code assuming nothing about controller behavior.
Pitfall 2: Blocking the Main Thread
Heavy processing causes visible lag:
- Avoid synchronous operations in polling loops
- Offload complex calculations
- Prioritize visual updates
Solution: Use Web Workers and requestAnimationFrame appropriately.
Pitfall 3: Poor Error Handling
Controllers disconnect unexpectedly:
- Users unplug during testing
- Wireless connections drop
- Browser permissions change
Solution: Implement comprehensive error handling with user-friendly messages.
Pitfall 4: Neglecting Mobile Users
Many users access testers on mobile devices:
- Touch interfaces need different considerations
- Bluetooth controller support varies
- Screen space is limited
Solution: Design mobile-first or ensure responsive fallbacks.
Pitfall 5: Overcomplicating the Interface
Feature creep ruins usability:
- Too many options overwhelm users
- Complex layouts confuse beginners
- Performance suffers from bloat
Solution: Focus on core functionality first, add advanced features progressively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a gamepad tester tool?
A gamepad tester tool is software that verifies gaming controller functionality. It displays real-time information about button presses, analog stick positions, and trigger values. These tools help diagnose issues like stick drift, unresponsive buttons, and calibration problems.
How do I test my controller for drift?
To test your controller for drift, use an online controller tester and leave your analog sticks untouched. Watch the stick position indicator—if it moves without input, you have drift. Measure the deviation from center to determine severity. Dead zone adjustments can compensate for minor drift.
Does the HTML5 Gamepad API work with all controllers?
The HTML5 Gamepad API supports most modern controllers, but compatibility varies. Xbox and PlayStation controllers generally work well. Third-party and older controllers may have mapping issues or limited functionality. Always check specific controller compatibility before relying on web-based testing tools.
Why doesn’t my controller work in the browser?
Controllers may not work in browsers due to several reasons: missing drivers, browser security restrictions, incorrect connection methods, or unsupported controller types. Try reconnecting the controller, using a different USB port, updating browser and drivers, or pressing a button to wake the controller.
Can I calibrate my controller using a web-based tester?
Web-based gamepad testers can display calibration information but typically cannot modify controller settings. For actual calibration, use your operating system’s controller settings or the manufacturer’s official software. Browser tools are best for verification rather than adjustment.
What’s the difference between dead zone and sensitivity?
Dead zone defines the area around stick center where inputs are ignored, preventing drift-induced movement. Sensitivity determines how quickly the stick reaches maximum value outside the dead zone. Both settings work together to create optimal controller feel for individual preferences.
How accurate are online controller testers?
Online controller testers are generally accurate for basic functionality verification. They reliably detect button presses, show approximate stick positions, and identify major issues like drift. However, precision measurements may vary between browsers and aren’t suitable for professional calibration purposes.
Conclusion
Building a reliable gamepad tester tool requires balancing technical complexity with user accessibility. Developers must navigate hardware variations, browser differences, and performance constraints while delivering intuitive experiences.
The lessons shared in this guide represent years of collective developer experience. From understanding the HTML5 Gamepad API’s nuances to implementing effective drift detection, each component contributes to a comprehensive testing solution.
Key Takeaways
- Master the Gamepad API – Understanding its capabilities and limitations is fundamental to building effective testing tools.
- Plan for diversity – Support multiple controller types, browsers, and use cases from the beginning.
- Prioritize performance – Laggy testing tools provide unreliable results and frustrate users.
- Implement thorough drift detection – This feature addresses one of gamers’ most common concerns.
- Design for all users – Accessibility and intuitive interfaces make tools useful for everyone.
- Test extensively – Quality assurance with real hardware prevents embarrassing bugs in production.
- Iterate based on feedback – User input reveals problems developers never anticipated.
Whether you’re building your first gamepad test application or improving an existing USB controller tester, these principles will guide you toward creating something truly useful for the gaming community.
The best testing tools combine technical excellence with thoughtful design. They empower users to diagnose problems quickly and confidently. By applying these lessons, you can build tools that gamers will trust and recommend.
External sources:
